
21 tips you should know to live a full and healthy life with diabetes.
Tabla de contenidos
What is type 2 diabetes?
Hello again!! It’s always nice seeing you here on our Blog. And if you are new, let us introduce ourselves to you; we are Diabetes Consciousness; a committed team to help you find solutions towards health.
This article has been created in response to our followers, who has been asking, basically, what is Type 2 Diabetes? Of course, this question can be taken for granted; however, it’s vital you can always feel well informed and secure about everything surrounding you related to this health condition you are experiencing.
Therefore, after engaging with our readers and looking over the comments they have left us, we acknowledged the importance of posting a crystal clear definition of Diabetes in our Blog.
We know that you have chosen to take an active role in your health journey, which is the main reason you are here.
Additionally to the well-explained definition, we invite you to glimpse into the bonus info we have added to this article, especially if you’d like to know how to live a long life with diabetes. As shocking as it sounds, we found a list of 10 foods diabetics should avoid, and they probably still don’t know because they think they are actually good for them! Don’t worry; we will share all of it with you.
So without further ado.
Before explaining what diabetes type 2 is, we know several people with diabetes are not used to clinical terms. Unfortunately, this scenario leads them to seek more and more information that ends up confusing them. Here you will be pleased to know this article is not the case.
Type 2 diabetes is a health condition that can affect our daily life. It mainly affects adults and middle-aged people, but nowadays is becoming moreover alarmingly in children and adolescents, mainly due to excess body weight and physical inactivity.
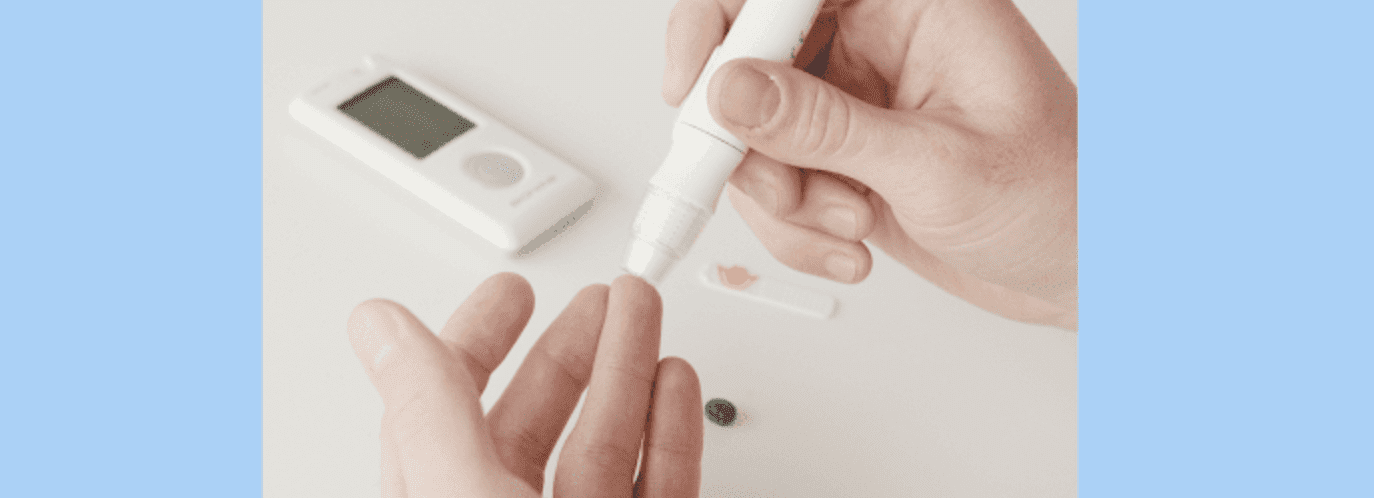

Type 2 diabetes is more common than type 1 diabetes.
According to the World Health Organization, in 2020 approximately 463 million adults worldwide had diabetes.
There are about 34.2 million people in the US with type 2 diabetes. Another 88 million people over the age of 18 have prediabetes, making it one of the top 10 causes of death in the United States and the whole world.
When we eat, the carbohydrates we ingest break down into simple sugars like glucose, which is crucial for all bodies as it works as fuel.
The substance usually responsible for transporting glucose to the cells to be used as energy is insulin. When the pancreas secretes this hormone, it regulates blood sugar according to the carbohydrates we have ingested.
What happens in type 2 diabetes is that the body isn’t capable of assimilating this glucose.
In the early stages of type 2 diabetes, the body’s cells do not fully react to insulin as they should, which is known as “Insulin resistance”.
In more advanced stages, if the disease is not treated, the pancreas, which has been producing a large amount of insulin that is not being used by the cells, becomes depleted and stops producing this hormone.
When this condition prolongs in time, glucose remains accumulated in the bloodstream, circulating and producing disorders in the chemistry and the normal functions of the body (this is why it is considered a metabolic alteration).
Finally, this condition leads to the deterioration of various organs of the body.
What are the risk factors for type 2 diabetes?
- Genetic and environmental factors (The risk of developing type 2 diabetes increases with the number of affected family members and can be triggered by lifestyle habits).
- A diet based on carbohydrates and sugars.
- Obesity

- Increased cholesterol.
- High triglycerides.
- High blood pressure.
- Sedentary lifestyle.
- Chronic stress.
- Hormonal changes during pregnancy (can cause gestational diabetes in some women).
How can you tell you have Diabetes?

- Excessive hunger.
- Excessive thirst.
- Dry mouth.
- Increased urination frequency.
- Permanent fatigue.
- Slow healing lesions and frequent infections.
- Blurred vision.
- Red and swollen gums.
- Numbness and tingling in the hands and feet.
- Sexual dysfunctions.
Some complications that can appear are:

- Atherosclerosis, known as the hardening of the arteries due to fat deposits that interfere with blood flow. Healthy arteries should normally reach organs such as the heart, the brain, the lungs, etc. This illness is often associated with type 2 diabetes patients.
- Higher risk of heart attack or stroke.
- Higher risk of serious eye diseases such as glaucoma or cataracts, leading to possible damage to the retina microvessels.
- hearing loss is very common in people with diabetes due to high blood glucose levels that damage the blood vessels of the inner ear.
- Neuropathies, pain, and numbness in the legs and feet, all due to nerve damage caused by blood sugar spikes.
- Type 2 diabetes also increases the risk of brain diseases; the higher the glucose level, the greater the risk of cognitive dysfunctions such as Alzheimer’s.
- Damage in the kidney’s functioning is another complication due to high blood glucose, increased blood pressure, and decreased renal blood circulation. This leads the kidney to dump its metabolic waste directly into the blood, causing damage to the central nervous system.
- Amputations and slow wound healing, leading to possible skin infection, mainly on the foot.
- Periodontitis, a chronic inflammatory disease in gums that can lead to tooth loss.
So what can you do to Treat and Prevent Type 2 Diabetes?

You can manage and prevent diabetes by adopting a new healthy lifestyle.
Regarding physical activity, we encourage you to gradually weight can be controlled by choosing personalized balanced eating plans. It is important to remember that a diet should not rely on refined carbohydrates and sugars. Instead, consider opting for whole foods high in fiber and increase protein consumption and healthy fats such as omega-3s.

The 10 foods that people with diabetes should avoid:
2- Trans fats. Since the body has no way to release these fats, they increase insulin.
3- White flours, even whole wheat flour. In general, they tend to inflame the digestive tissues and are not suitable for diabetics. It’s better to consume whole grains.
4- Whey protein has a lot of Leucine which raises insulin and blood glucose.
5- Dairy products, in general, have casein and inflame the gastric mucosa. This promotes insulin to rise.
6- Conventional box cereals, granola, or muesli. We suggest you make homemade granola with seeds and oats.
7- Instant coffee mixes contain sweeteners that raise blood glucose.
8- Kinds of honey and syrups, especially agave honey. Even though these are natural, they tend to have a lot of fructose.
9- Dehydrated fruits have more fructose than fresh fruit due to their production process.
Fruit juice, fiber is lost and fructose multiplies.
MORE VIDEOS:
Type 2 Diabetes Definition
TOP PLAYLIST:
https://link.diabetesconsciousness.com/diab2-def-playlist—————————————










